As the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) develops new control technique guidelines, the definition of the RACT (Reasonably Available Control Technology) standards changes on a state level.
The EPA has defined RACT as: “the lowest emission limitation that a particular source is capable of meeting by the application of control technology that is reasonably available considering technological and economic feasibility.”
Failing to keep up in this ever-changing regulatory landscape can be expensive and time-consuming. "Continuous Compliance" is now the standard the EPA expects industry to meet. Lack of knowledge of the changes in regulatory standards or failure of a control device can result in fines and additional permit restrictions that inhibit production and reduce profits.
Air Pollution Acronyms
NESHAPs - National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants
NSPS - New Source Performance Standards
RACT - Reasonably Available Control Technology standards
PSD - The Prevention of Significant Deterioration program
VOC - Volatile Organic Compound
HAPs - Hazardous Air Pollutants
SCFM - Standard Cubic Feet per Minute
TRE - Thermal Rate Efficiency
LEL - Lower Explosive Limit
NOx - Nitrogen Oxides
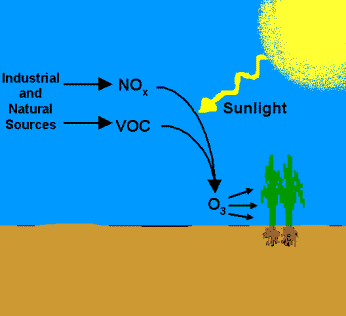
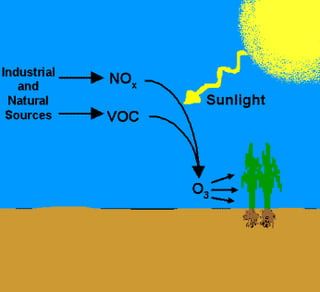
VOCs are pre-cursors of ground level ozone or smog. Ground level ozone is created by the reaction of VOCs with NOx in the presence of sunlight. Ozone has the same chemical structure whether it occurs miles above the earth or at ground-level, and it can be "good" or "bad,“ depending on its location in the atmosphere.
Hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) are chemicals which can cause adverse effects to human health or the environment. There are more than 188 of these pollutants, including substances that cause cancer as well as neurological, respiratory, and reproductive effects. The EPA requires more stringent control of HAPs, and EPA regulations may affect the final air pollution technology used.
Examples of toxic air pollutants include benzene, which is found in gasoline; perchloroethylene, which is emitted from some dry cleaning facilities; and methylene chloride, which is used as a solvent and paint stripper by a number of industries.
The ideal air pollution control solution for any industrial operator - especially in chemical processing industries where productivity and safety are vitally important - involves controls that are proven reliable in the harshest environments and that are engineered to meet not only today's requirements, but tomorrow's as well.
Operators of facilities are always under scrutiny from environmental protection regulatory agencies. Overlapping and frequently confusing regulations that affect the industry are enforced at the local, state, and federal levels. To make life even more difficult for the plant operator, the VOC and HAP control standards they are charged with managing are often a moving target.
Catalytic Products International remains ever vigilant to new EPA related standards, regulations, and now new methods of enforcement. With almost 50 years of experience and the most complete line of air pollution control solutions to call on, we have the Engineering Expertise to ensure we are providing the best solution for your most challenging air pollution control problems.
Here at Catalytic Products International, we’re working hard to provide the topical and important information about regulatory issues that impact our customers' business. We are also hard at work providing helpful resources for maintenance and aftermarket support of your air pollution control equipment. Feel free to join us on Twitter or LinkedIn for the most recent and up-to-date information about air pollution control, energy conservation, and your business.
Our Resouce Center contains links to many e-books, blogs, and case studies.