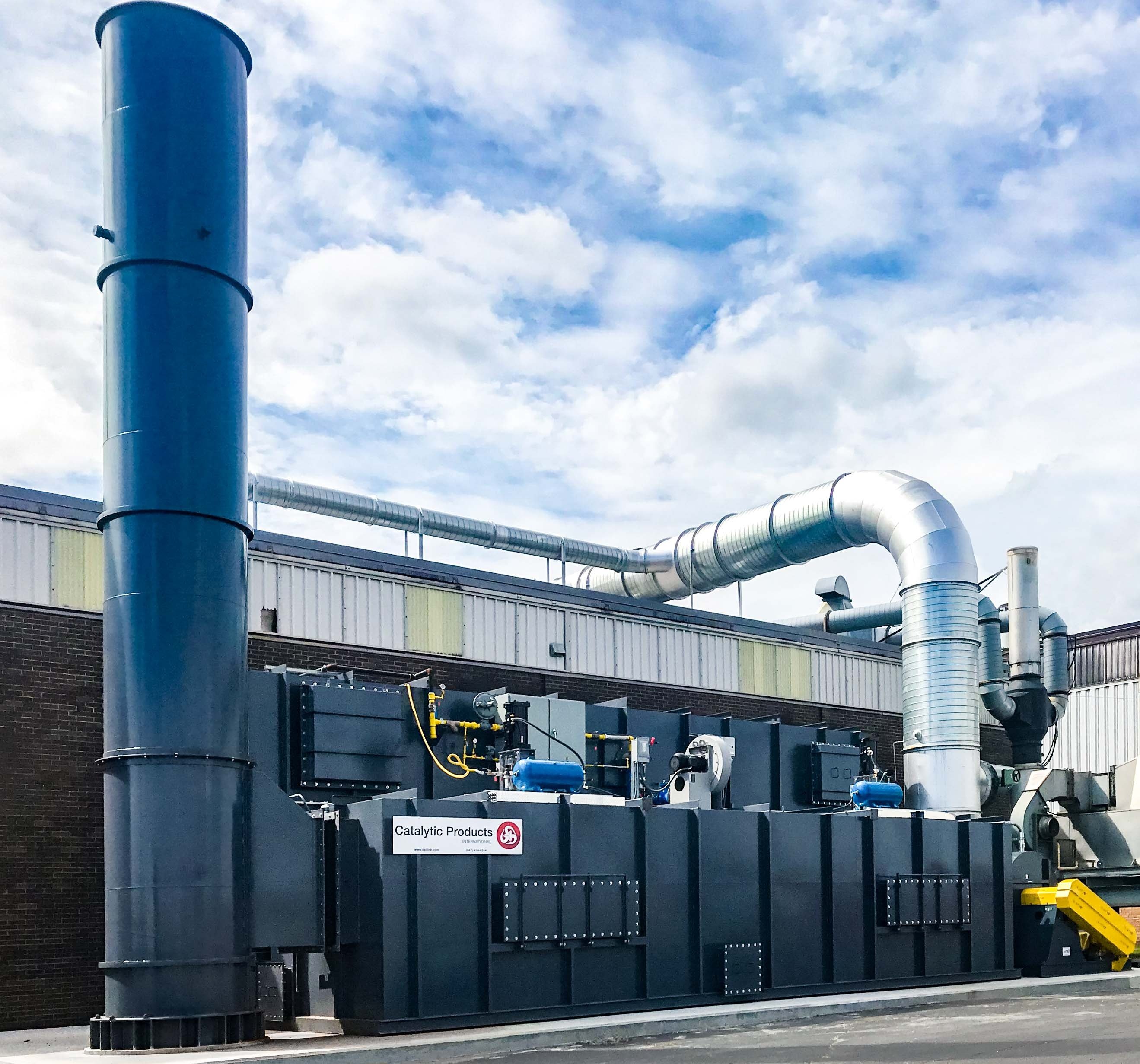
Our first encounters with our customers often start with this statement; “I was told that I need a RTO.” That’s obviously a big statement which usually leads to many more questions to precisely determine where we can help. This also means that the person with interest has some sort of air pollution control problem that may involve volatile organic compounds (VOC), carbon monoxide (CO) or odorous emissions.
It may be helpful to understand the basic reason anyone would need a Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO).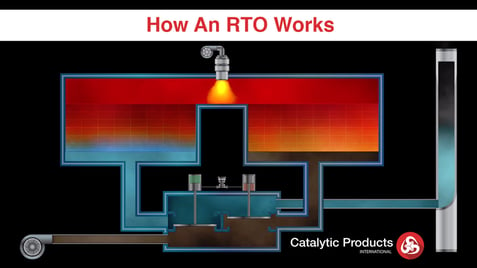
WHAT IS AIR POLLUTION?
Many industrial processes produce or use volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). VOCs and HAPs are hydrocarbons that are necessary components for industries such as printing, painting, or coating. VOCs are also emitted from many processing facilities in the manufacture of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and foods.
Pollution control equipment is installed on these processes to prevent the VOCs and other emissions from reacting with nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the presence of heat and sunlight and forming ground level ozone. This is the basis for continuous Clean Air Act legislation and enforcement by EPA regulatory agencies.
Today’s environmental concerns have led many industries to search for more effective pollution control methods. While many technologies are available to simply control VOCs and other emissions, oxidation technologies routinely exceed many of the world’s clean air regulations. When applied appropriately, oxidation technologies such as catalytic and thermal treatment provide continuous performance with the lowest treatment cost. In this blog, we’ll explore more about RTOs and how this type of thermal treatment can help eliminate VOCs and other pollutants from industrial processes.
REGENERATIVE THERMAL OXIDATION FOR AIR POLLUTION CONTROL

Thermal treatment of VOCs and other air pollutants works by a simple reaction of the harmful air pollutants with oxygen and heat. In this environment, the VOCs are converted to carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and usable heat. These harmless by-products are released to the atmosphere or use an energy recovery technique to further lower the operational costs.
A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) is an air pollution control device that is designed to destroy VOC, HAP, and Odorous compounds in order to meet air pollution control regulations. RTOs have gained worldwide acceptance as viable pollution control alternatives due to ever-rising fuel costs and environmental agencies’ efforts to clean up the lowest emitters of VOCs.
Let’s break the phrase Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer down into its rudimentary parts:
- Regenerative: A means of heat recovery whereby the energy of hot clean gas is used to pre-heat the incoming dirty gas and work to lower the auxiliary fuel required for operation.
- Thermal: The process of using heat energy to convert or oxidize the pollutants (typically hydrocarbons).
- Oxidizer: A device that utilizes time, temperature, and turbulence to effectively convert pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Understanding regenerative thermal oxidation for air pollution control is just the beginning in deciding whether or not you need a regenerative thermal oxidizer. In our next blog, we’ll look more closely at the Regenerative Thermal Oxidation process and discuss some of the different options for Regenerative Thermal Oxidizers. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
Link to Part 2: Do I Need a RTO? Part 2: How Does Regenerative Thermal Oxidation Work?








